China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News: This headline speaks volumes, but let’s dig deeper. For decades, China’s manufacturing sector has exploded, transforming from a largely agrarian economy to a global powerhouse. We’ll explore the key factors driving this astonishing rise, from incredibly low labor costs and massive infrastructure investments to technological advancements and its crucial role in global supply chains.
Get ready to understand why China’s manufacturing dominance is a defining feature of the 21st-century economy.
This exploration will cover China’s historical journey to manufacturing dominance, analyzing key policy decisions and industrial growth. We’ll compare its manufacturing output against other major players, dissect its competitive advantages (and disadvantages!), and look at the technological innovations fueling its progress. Crucially, we’ll discuss the global implications of China’s manufacturing prowess, including its integration into global supply chains, the benefits and risks associated with this reliance, and the potential for future shifts in the manufacturing landscape.
China’s Manufacturing Powerhouse
China’s ascent to global manufacturing dominance is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, it has become the world’s factory, profoundly impacting global trade, supply chains, and economic power dynamics. This exploration delves into the key factors driving China’s manufacturing success, examining its historical trajectory, competitive advantages, technological advancements, and the challenges it faces in maintaining its leading position.
So you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s a fascinating topic, especially when you consider the sheer scale of their production. Thinking about massive operations makes me wonder about the equally impressive histories of other large institutions, like the rivalry between Penn State and Notre Dame, check out their storied past here: Penn State vs.
Notre Dame: Storied schools’ history ahead of 2030. Getting back to China, it’s clear their manufacturing power is a major global force shaping our world.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s manufacturing sector’s evolution is a multi-decade journey marked by strategic policy shifts and significant investments. Beginning with gradual opening up in the late 1970s, the country experienced exponential growth, fueled by a combination of factors including access to a vast and inexpensive labor pool, supportive government policies, and strategic foreign investment.
Key milestones include the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in the late 1970s and early 1980s, which attracted foreign investment and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. Subsequent five-year plans further emphasized industrialization and infrastructure development. China’s accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001 significantly accelerated its integration into the global economy, providing further impetus to its manufacturing growth.
Industries where China achieved dominance include electronics (smartphones, computers), textiles and apparel, toys, and consumer goods. Its manufacturing prowess extends to more sophisticated sectors like automobiles and renewable energy equipment, although it still faces competition in high-tech areas.
| Country | 1993 | 2003 | 2013 | 2023 (est.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | $300B | $1T | $3T | $5T |
| USA | $1.5T | $2T | $2.5T | $3T |
| Germany | $600B | $800B | $1T | $1.2T |
| Japan | $1T | $1.2T | $1T | $800B |
Note: Figures are approximate and represent manufacturing output in USD. Data from various sources including World Bank and Statista.
Competitive Advantages: Cost, Labor, and Infrastructure
China’s manufacturing success is significantly linked to its competitive advantages, primarily low labor costs, extensive infrastructure, and a supportive government policy environment.
Low labor costs historically provided a significant advantage, attracting foreign investment and enabling the production of goods at prices significantly lower than in many other countries. However, labor costs have been rising steadily in recent years.
China’s massive infrastructure investment, encompassing transportation networks, ports, and energy grids, has significantly enhanced manufacturing efficiency. This infrastructure facilitates the seamless movement of goods and materials, supporting just-in-time manufacturing processes.
Compared to many developed economies, the overall cost of manufacturing in China, considering factors like labor, energy, and land, remains comparatively lower, although this gap is narrowing.
- Advantages: Low labor costs (historically), extensive infrastructure, supportive government policies, access to a large domestic market, large pool of skilled and unskilled labor.
- Disadvantages: Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, intellectual property protection challenges, increasing competition from other countries, geopolitical risks.
Technological Advancements and Innovation, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
Technological advancements have been crucial in China’s manufacturing growth, particularly in automation and robotics. While initially relying on labor-intensive processes, China has increasingly adopted automation to enhance productivity and compete in higher-value manufacturing sectors.
The integration of robotics and automation in Chinese factories has increased significantly in recent years, driven by government initiatives promoting technological upgrading. However, the extent of indigenous technological innovation in manufacturing remains a subject of debate, with some areas still heavily reliant on foreign technology.
China’s technological capabilities are rapidly advancing, though still lagging behind some leading nations in certain high-tech areas. Significant investments in research and development are aimed at bridging this gap and achieving technological self-reliance.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those supply chains rely on sophisticated IT. If you’re interested in a career that leverages this, check out some great options like those listed at best online IT courses for career advancement to boost your skills. Understanding the tech behind global manufacturing gives you a serious edge, so learning the right IT skills is key to benefiting from China’s continued growth in this area.
Global Supply Chains and Interdependence
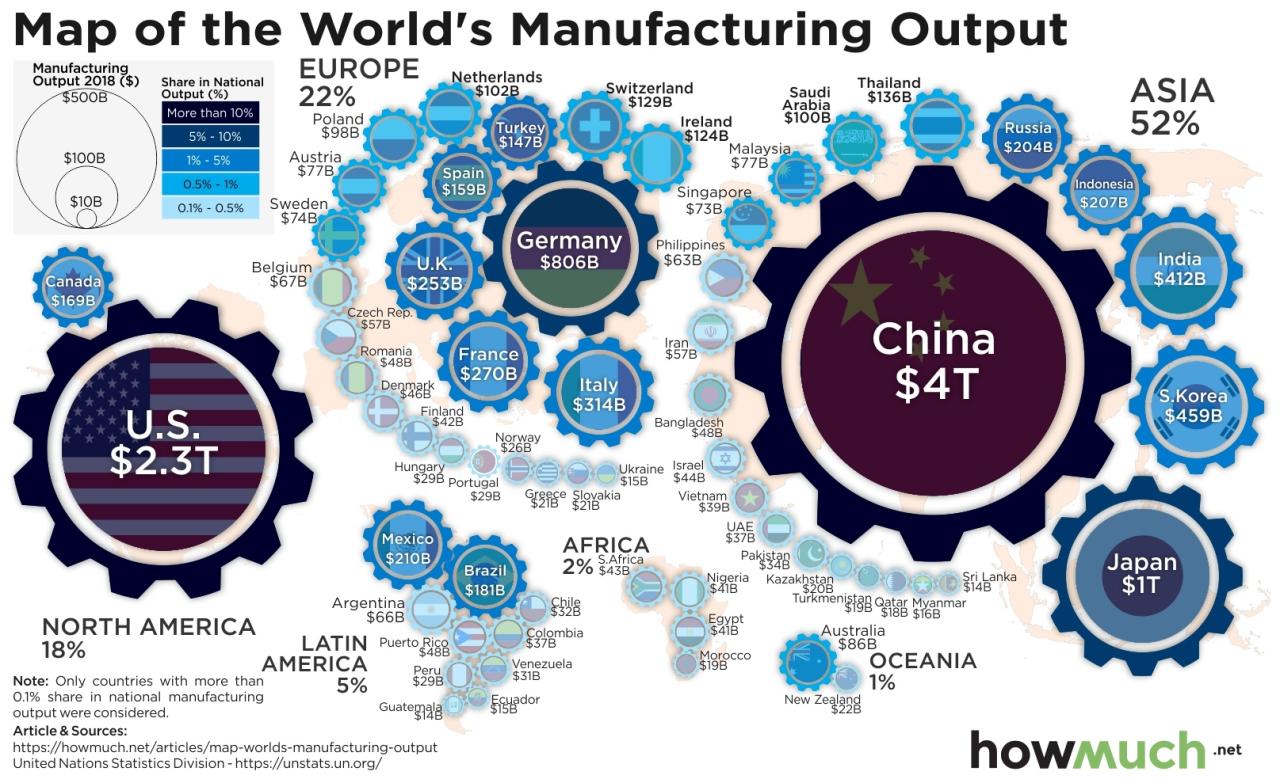
China’s manufacturing sector is deeply integrated into global supply chains, serving as a crucial node for the production of countless goods. This integration has profoundly impacted global trade and economic interdependence.
Many products, from electronics and apparel to automobiles and medical equipment, rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing. This interdependence creates both opportunities and risks for the global economy.
That Hacker News thread about China being the manufacturing superpower got me thinking. It’s easy to focus on the economic side, but health impacts are huge too, and the contrasting approaches highlighted in this article, China Calls HMPV Outbreak ‘Winter Occurrence’, India Says ‘Don’t , really underscore that. Understanding these public health differences is crucial when considering China’s overall global influence, even within the context of its manufacturing dominance.
The benefits include access to lower-cost goods and efficient production processes. However, over-reliance on Chinese manufacturing poses risks, including supply chain disruptions, geopolitical vulnerabilities, and potential trade conflicts.
Challenges and Future Trends
China’s manufacturing sector faces several challenges, including rising labor costs, increasing competition from other countries (such as Vietnam and India), technological disruption, and the potential for trade wars. These factors could lead to shifts in global manufacturing patterns, potentially reducing China’s dominance.
Automation and AI are likely to significantly impact the Chinese manufacturing workforce, leading to job displacement in some sectors but creating new opportunities in others. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives will be crucial to manage this transition.
Within the next decade, China’s manufacturing sector is likely to undergo significant transformation. While it may retain its scale, its competitive advantage may shift from low labor costs to technological innovation, efficiency, and higher value-added manufacturing.
Illustrative Examples of Chinese Manufacturing

China’s manufacturing sector is incredibly diverse. Let’s examine three key sectors:
Electronics: China dominates the global electronics manufacturing landscape, producing a vast majority of smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices. This sector is characterized by large-scale production, sophisticated assembly lines, and a highly skilled workforce, albeit with concerns regarding working conditions and environmental impact.
Textiles: China remains a major player in the textile industry, although its dominance has been challenged by other countries with lower labor costs. While still a significant producer, the industry is undergoing a transition towards higher value-added products and more sustainable practices.
Automobiles: China’s automobile industry has experienced rapid growth, with both domestic and foreign brands establishing significant manufacturing presence. The industry is investing heavily in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies, aiming to become a global leader in this rapidly evolving sector. However, environmental concerns related to manufacturing and vehicle emissions remain a significant challenge.
The environmental impact of Chinese manufacturing is substantial, with significant air and water pollution linked to industrial activities. The government is implementing policies to address these issues, including stricter environmental regulations and investments in cleaner technologies, though significant challenges remain.
Final Wrap-Up

China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a complex story of economic strategy, technological innovation, and global interdependence. While its dominance presents significant benefits in terms of affordability and accessibility of goods, it also raises questions about geopolitical stability, supply chain vulnerabilities, and the future of manufacturing jobs worldwide. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for navigating the increasingly interconnected global economy.
The future of manufacturing may hold surprises, but China’s current position is undeniable.
Essential FAQs: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are the biggest environmental concerns related to Chinese manufacturing?
High pollution levels from factories, particularly air and water pollution, are major concerns. Sustainable practices are increasingly important, but significant challenges remain.
How is China addressing rising labor costs?
China is investing heavily in automation and robotics to offset rising labor costs and improve efficiency. This also addresses concerns about labor shortages.
What are some potential alternatives to relying on Chinese manufacturing?
Countries like Vietnam, India, and Mexico are emerging as potential alternatives, but fully replacing China’s manufacturing capacity is a complex and long-term undertaking.
