How to operate a drone introduces the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This guide delves into the essential skills and knowledge needed to safely and effectively pilot a drone, from pre-flight checks and understanding regulations to mastering camera operation and performing basic maintenance. Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll cover everything from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different flight modes to capturing stunning aerial photography and troubleshooting common issues. Learn about essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and advanced techniques to elevate your drone piloting experience. Prepare for a journey that blends practical instruction with inspiring insights into the capabilities of this increasingly popular technology.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding local regulations, and planning for potential emergencies. Failure to do so can lead to accidents and legal repercussions.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition. The following checklist helps in this process.
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage or cracks | Replace damaged propellers | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Charge battery if necessary; replace if damaged | Avoid using damaged or swollen batteries. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper function | Tighten screws if loose; recalibrate if necessary | Ensure the gimbal is securely mounted. |
| Camera | Verify lens clarity and functionality | Clean lens if necessary | Check for any obstructions. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal | Relocate to an area with better signal if needed | Sufficient satellites are needed for stable flight. |
| Flight Controller | Check for any visible damage | Contact support if any issues are found | The flight controller is the drone’s brain. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any damage or debris | Clean motors if necessary | Ensure smooth rotation of each motor. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires adherence to local laws and regulations. Ignoring these can result in hefty fines, legal action, and even imprisonment. Always check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific rules in your area. These regulations often include restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and areas where drone flight is prohibited (e.g., near stadiums, government buildings, or densely populated areas).
For example, flying within a no-fly zone could lead to a fine of several thousand dollars, drone confiscation, or even criminal charges.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires learning about regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently take to the skies and master the art of drone piloting.
Safe Drone Operation Distances
Maintaining safe distances from people and obstacles is paramount. The following visual representation provides a guideline:
Drone
(100ft)
——————————————————–
People (minimum 50ft) Obstacles (minimum 25ft)
——————————————————–
Note: These distances are minimum recommendations and might need to be adjusted depending on local regulations and specific circumstances.
Emergency Procedures
Being prepared for emergencies is essential. Loss of signal and low battery are common scenarios requiring immediate action.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately engage “Return to Home” (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone back to a safe landing zone, prioritizing a controlled descent over speed.
- Low Battery: Initiate RTH immediately. If RTH is unavailable or fails, prioritize a controlled landing in a safe, open area. Avoid attempting risky maneuvers.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of a typical drone controller and guides you through basic flight maneuvers.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basic maneuvers, and for a comprehensive guide on this, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable flights, ultimately leading to proficient drone operation.
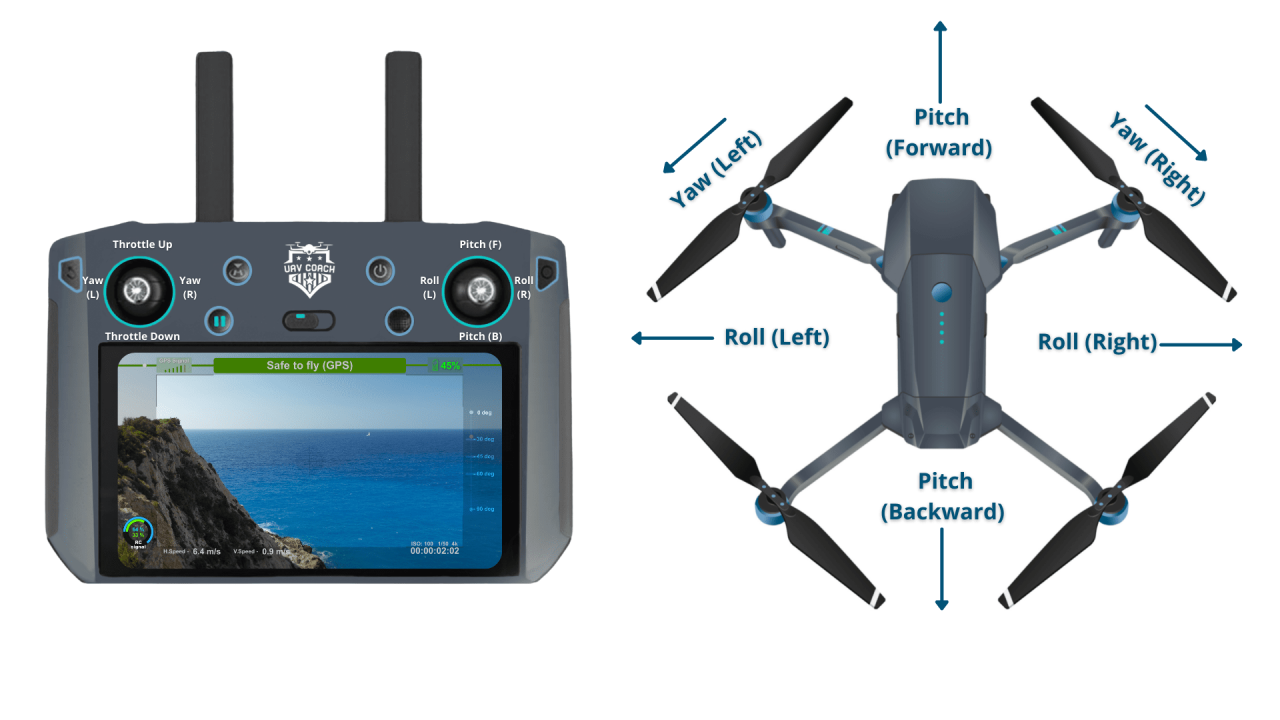
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks for flight control and various buttons for additional functions. The left stick typically controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude, while the right stick controls the drone’s movement forward/backward and left/right. Buttons on the controller often manage camera functions, flight modes, and RTH. Consult your drone’s manual for specific control layouts.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. GPS mode utilizes satellite data for precise positioning and stable flight, making it ideal for beginners. Attitude mode, on the other hand, offers more direct control but requires greater skill to prevent unintended movements. Understanding the differences between these modes is crucial for adapting to different flight conditions.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Pre-flight checks: Complete all pre-flight checks Artikeld above.
- Power on: Turn on the drone and controller.
- Calibration: Allow the drone to calibrate its GPS and sensors.
- Takeoff: Gently push the throttle stick upwards to initiate takeoff.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude and position using the control sticks.
- Maneuvers: Practice basic maneuvers such as moving forward, backward, left, and right.
- Landing: Slowly lower the throttle stick to initiate a controlled descent and landing.
- Power off: Turn off the drone and controller.
Smooth Drone Maneuvers
Smooth and controlled maneuvers are achieved through gentle stick movements and precise adjustments. Avoid abrupt movements, especially during takeoff and landing. Practice makes perfect. Smooth turns are accomplished by using the left joystick to rotate while simultaneously adjusting the right joystick to maintain forward momentum.
Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and mastering various shooting techniques. This section will explore camera settings, shooting techniques, and common mistakes to avoid.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. ISO controls the sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but can introduce noise. Shutter speed determines the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light; faster shutter speeds freeze motion but require more light, while slower speeds allow more light but can result in motion blur.
Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens; wider apertures (lower f-stop numbers) create shallow depth of field, blurring the background, while narrower apertures (higher f-stop numbers) provide greater depth of field, keeping both foreground and background in focus.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Different Shots
- Landscape: Use a lower ISO, moderate shutter speed, and a narrower aperture for sharp details across the entire scene.
- Close-up: Use a higher shutter speed to freeze motion and a wider aperture to blur the background.
- Aerial Panoramas: Use a low ISO and moderate shutter speed, ensuring consistent exposure across the stitched images.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Drones offer unique angles and perspectives unavailable with traditional cameras. Experiment with different altitudes, angles, and movements to capture creative and engaging shots. Consider using the drone’s ability to tilt the camera for dynamic perspectives.
Common Camera Mistakes, How to operate a drone
- Overexposed or underexposed images: Pay close attention to the histogram and adjust exposure settings accordingly.
- Blurry images: Use a higher shutter speed to freeze motion and ensure the drone is stable.
- Poor composition: Plan your shots carefully and use the drone’s screen to preview the composition.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable performance. This section covers routine maintenance, common malfunctions, and troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent major issues. This should include visual inspections of all components, cleaning propellers and the drone body, and checking battery health.
- Weekly: Inspect propellers for damage, clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Monthly: Check battery health and charging cycles, inspect motors and gimbal.
- Quarterly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components, tighten screws as needed.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include battery problems, motor failures, and GPS signal loss. Understanding potential causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Battery problems: Check battery level, replace if necessary, ensure proper charging.
- Motor failures: Inspect motors for damage, replace faulty motors.
- GPS signal loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS signal, recalibrate GPS.
Drone Battery Types
| Battery Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | High energy density, lightweight, requires careful handling. |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | Higher voltage than LiPo, improved flight time. |
| LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Safer than LiPo, longer lifespan, lower energy density. |
Advanced Drone Techniques and Applications
This section explores advanced drone techniques and applications beyond basic flight and photography.
Waypoint and Automated Flight Planning
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path, enabling automated flights and consistent shot repetition. This is particularly useful for creating cinematic shots or conducting inspections.
Capturing Smooth, Cinematic Footage

Smooth, cinematic footage requires careful planning and execution. Use smooth, controlled movements, avoid sudden changes in direction or altitude, and consider using accessories like gimbals for added stability.
Drone Model Comparison
Different drone models offer varying capabilities, from flight time and camera quality to features like obstacle avoidance and intelligent flight modes. Researching different models and their specifications is crucial for choosing the right drone for your needs.
Hypothetical Drone Flight Plan

A hypothetical flight plan for filming a construction site might involve pre-programmed waypoints to capture progress on different parts of the site, with specific camera angles and altitudes for detailed shots. Safety considerations, such as avoiding workers and maintaining safe distances, would be paramount.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding endeavor, combining technical skill with a deep appreciation for safety and responsible flight. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently explore the boundless possibilities of aerial photography, videography, and beyond. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect airspace regulations, and continue learning to hone your skills and expand your capabilities. The skies await your exploration!
Detailed FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Look for models with intuitive controls and robust safety features.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid letting it completely discharge. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific charging recommendations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately attempt to return the drone to its home point (if equipped). If that fails, engage emergency landing procedures Artikeld in your drone’s manual and contact local authorities if necessary.
How do I obtain necessary permits or licenses for drone operation?
Regulations vary by location. Research and comply with all local, state, and federal laws regarding drone operation and registration before flying.
